what are the different types of plant resistance?
Explore the different types of plant resistance, including ecological, genetic, and evolutionary strategies that help plants defend against pests and pathogens.
Explore the different types of plant resistance, including ecological, genetic, and evolutionary strategies that help plants defend against pests and pathogens.
Although it might seem like plants live a carefree life filled with sunbaths and rain showers, most plants live in hostile environments where they have to deal with pests, harsh weather, pollution, and scarce resources. Surviving and even thriving in such environments requires that they adapt and gain advantages that will enable them to: Adapt…
In recent years [and for generations among indigenous populations], companion planting has emerged as a common technique aimed at exploiting the benefits of the relationships between specific plants to naturally improve crop flavor, health, and vigor. More simply, companion planting is a type of polyculture where two plant species are grown together because it is…
Plant structure and appearance varies throughout a plant’s lifecycle. It is natural for leaves to brown and fall and it is not uncommon for fruits and flowers to vary in size and shape. However, there is a range of factors that can lead to more intensive damage and irregularities. These factors are known as plant…
All healthy ecosystems contain a complex system of microbes, insects, plants, and animals that interact to maintain balance and contribute to the well-being of a given space. Companion planting is a targeted effort to exploit the benefits of the relationships between specific plants to improve production vitality. More simply, companion planting is a specific type…
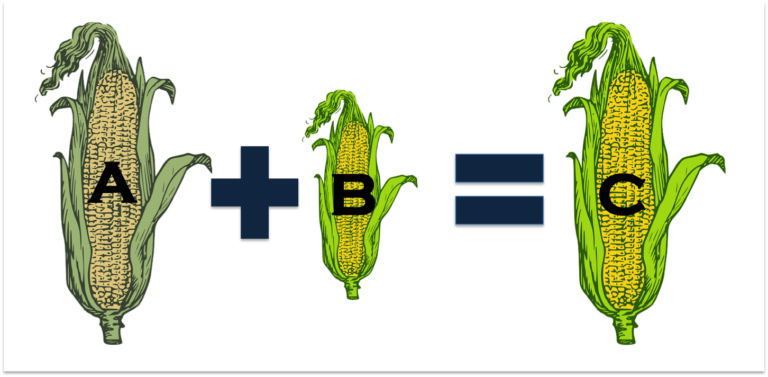
Hybrid plants are a crossing between two selected parent plants achieved via controlled pollination (see how are plants propagated). The seeds produced by this process are called F1 or F1 Hybrids. These hybrids will exhibit very specific qualities. Hybrids have quickly come to dominate the seed market. However, in spite of their increased market presence…
New plants are created via plant propagation of which there are two types: sexual and asexual. With sexual propagation, there are two sources of parental DNA resulting in the creation of a third living organism. Sexual propagation involves the floral components of the plant and is the result of the pollination of megagametophyte (egg). There…
Biological control as it relates to horticulture and agriculture is the use of parasites, pathogens and predators to control pest populations and damage. These biological agents are known as natural enemies. The benefits offered by these biological agents is supported via conservation, augmentation and classical biological control tactics. Most parasites, pathogens and predators are highly…
Loss of Turgor Pressure (decrease in water pressure within plant cell walls) Causes: abiotic factors, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, insects Examples: Ralstonia solanacearum, Verticillium dahliae, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Enations (scaly leaflike structures that lack a vascular system) Causes: viruses Examples: Cherry raspberry leaf virus, Pea enation mosaic virus Stunting (dwarfing or loss of vigor) Causes:…
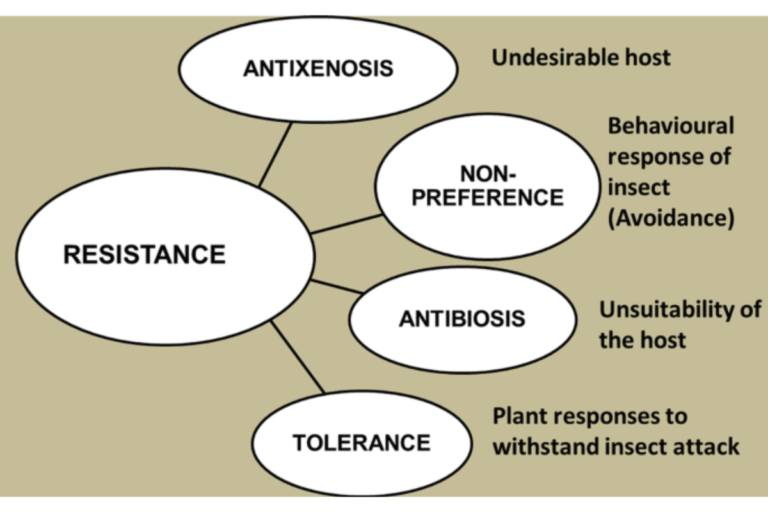
Plant tolerance and plant resistance are ways that plants deal with stressors in their environment. Resistance and tolerance are plants’ best defense mechanisms. At the most basic level, the difference between tolerance and resistance is related to how the plant defends itself. In the case of tolerance, the plant has strategies that helps it to…