10 common plant disease symptoms
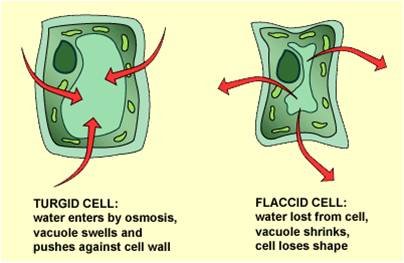
Loss of Turgor Pressure (decrease in water pressure within plant cell walls)
Causes: abiotic factors, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, insects
Examples: Ralstonia solanacearum, Verticillium dahliae, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
Enations (scaly leaflike structures that lack a vascular system)
Causes: viruses
Examples: Cherry raspberry leaf virus, Pea enation mosaic virus

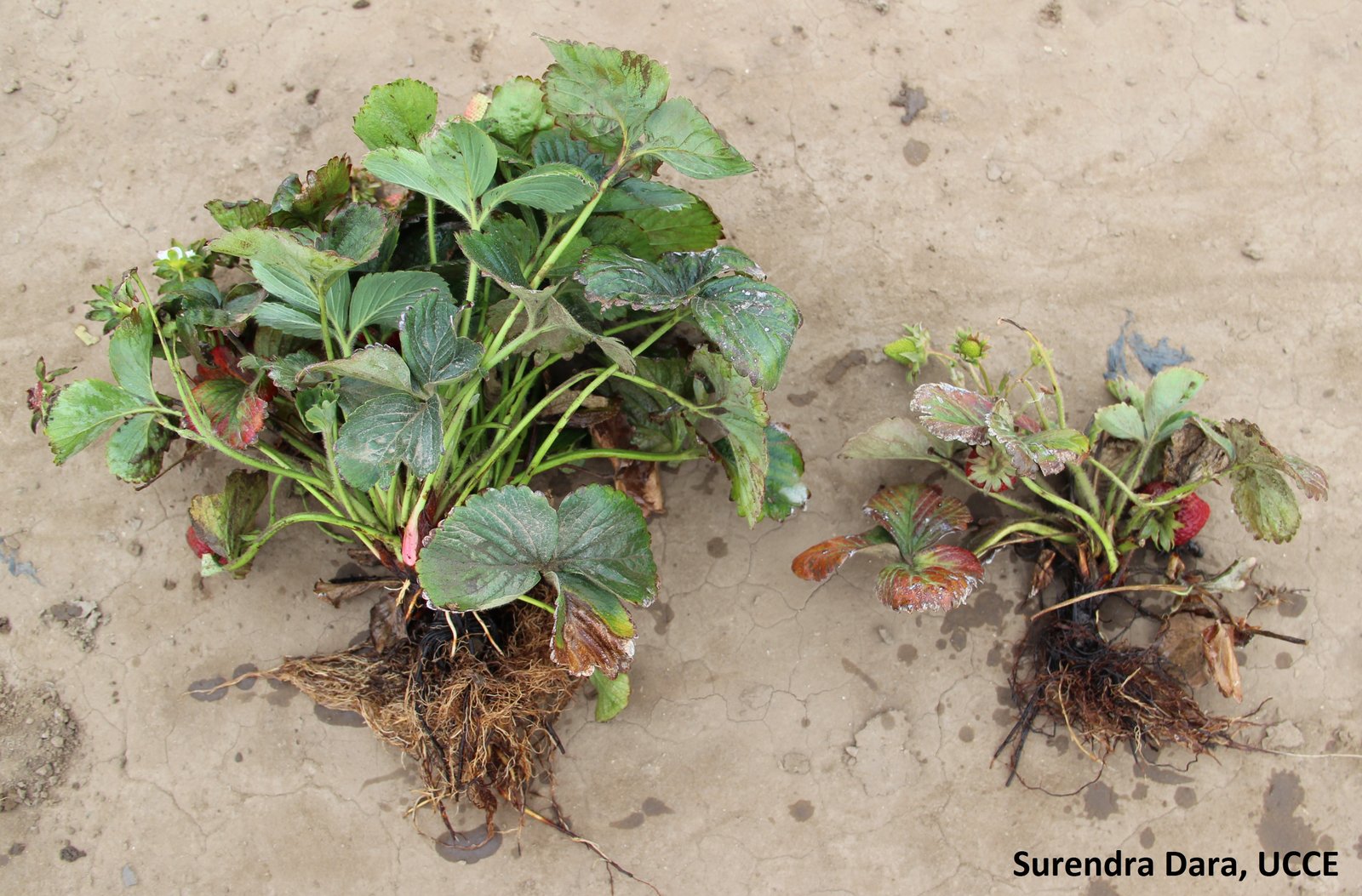
Stunting (dwarfing or loss of vigor)
Causes: viruses, phytoplasma, fungi, nematodes
Examples: Rhizoctonia, Strawberry lethal yellows

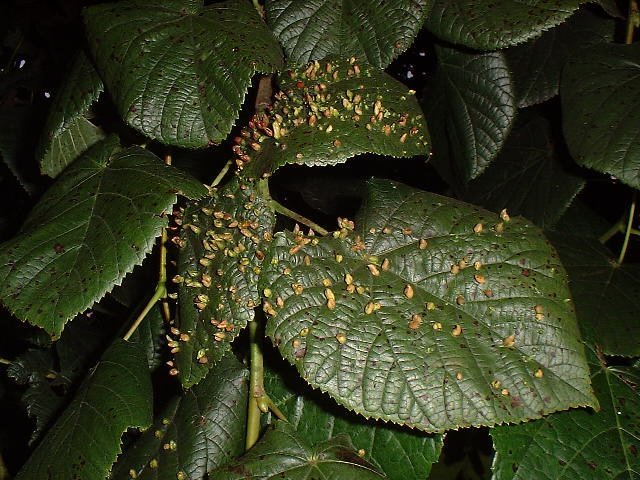
Witches’ Broom (dense clustering of abnormally small twigs)
Causes: phytoplasma, fungi, insects, mites
Examples: Ash yellows phytoplasma, Sphaerotheca sp.

Galls (abnormal growths)
Causes: fungi, nematodes, mites
Examples: Gymnosporangium sabinae, Meloidogyne spp.

Fruit and Seed Deformation (malformed fruit or seeds)
Causes: abiotic factors, viruses, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, insects
Examples: Catfacing tomatoes, Little cherry disease, Spiroplasma citri, Thrips palmi

Tumors (aggregates of cells that have multiplied excessively)
Causes: viruses, bacteria
Examples: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Cryphonectria parasitica

Gummosis (oozing of sap from wounds/cankers on fruit trees)
Causes: abiotic factors, bacteria, fungi, insects, injury to the cutting sites
Examples: Pseudomonas syringa, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides

Rot (decay)
Causes: bacteria, fungi
Examples: Arruina carotovora, Ralstonia solanacearum, Phomopsis obscurans, Botrytis cinerea

Necrosis (death of cells or tissues)
Causes: abiotic factors, viruses, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, insects
Examples: Xanthomonas axonopodis, Fusarium oxysporum, Milbe Tetranychus cinnabarinus

For more information about plant diseases read:
A Brief Introduction to Plant Diseases




2 Comments
Comments are closed.